NVTabular | Documentation
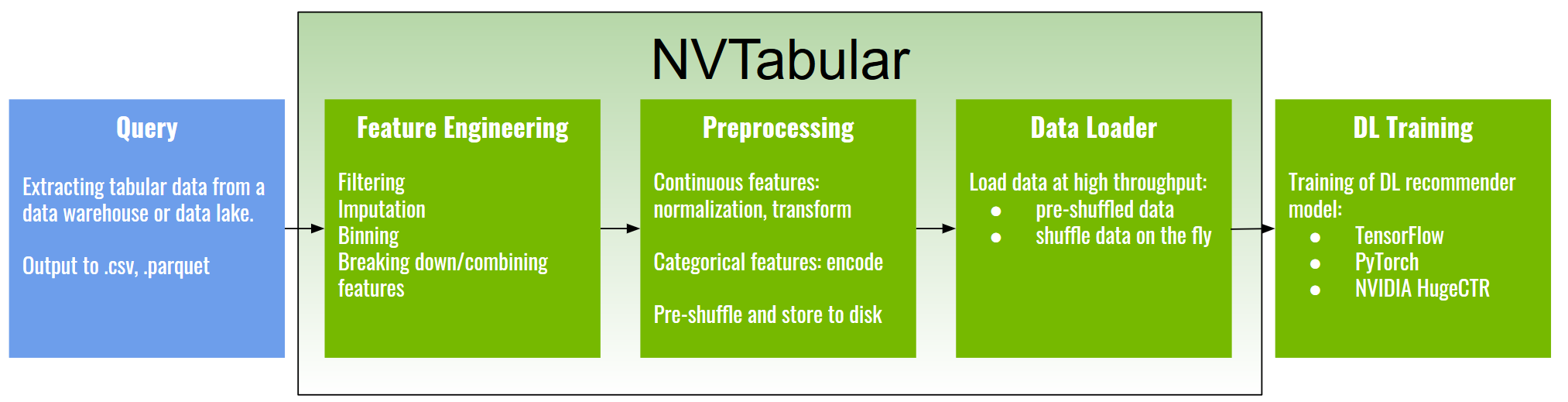
NVTabular is a feature engineering and preprocessing library for tabular data that is designed to easily manipulate terabyte scale datasets and train deep learning (DL) based recommender systems. It provides high-level abstraction to simplify code and accelerates computation on the GPU using the RAPIDS Dask-cuDF library. NVTabular is designed to be interoperable with both PyTorch and TensorFlow using dataloaders that have been developed as extensions of native framework code. In our experiments, we were able to speed up existing TensorFlow pipelines by nine times and existing PyTorch pipelines by five times with our highly-optimized dataloaders.
NVTabular is a component of NVIDIA Merlin Open Beta. NVIDIA Merlin is used for building large-scale recommender systems. With NVTabular being a part of the Merlin ecosystem, it also works with the other Merlin components including HugeCTR and Triton Inference Server to provide end-to-end acceleration of recommender systems on the GPU. Extending beyond model training, with NVIDIA’s Triton Inference Server, the feature engineering and preprocessing steps performed on the data during training can be automatically applied to incoming data during inference.
Benefits
When training DL recommender systems, data scientists and machine learning (ML) engineers have been faced with the following challenges:
Huge Datasets: Commercial recommenders are trained on huge datasets that may be several terabytes in scale.
Complex Data Feature Engineering and Preprocessing Pipelines: Datasets need to be preprocessed and transformed so that they can be used with DL models and frameworks. In addition, feature engineering creates an extensive set of new features from existing ones, requiring multiple iterations to arrive at an optimal solution.
Input Bottleneck: Data loading, if not well optimized, can be the slowest part of the training process, leading to under-utilization of high-throughput computing devices such as GPUs.
Extensive Repeated Experimentation: The entire data engineering, training, and evaluation process can be repetitious and time consuming, requiring significant computational resources.
NVTabular alleviates these challenges and helps data scientists and ML engineers:
process datasets that exceed GPU and CPU memory without having to worry about scale.
use optimized dataloaders to accelerate training with TensorFlow, PyTorch, and HugeCTR.
focus on what to do with the data and not how to do it by using abstraction at the operation level.
prepare datasets quickly and easily for experimentation so that more models can be trained.
NVTabular provides faster iteration on massive tabular datasets during experimentation and training. NVTabular helps ML/Ops engineers with deploying models into production by providing faster dataset transformation. This makes it easy for production models to be trained more frequently and kept up to date, helping improve responsiveness and model performance.
To learn more about NVTabular’s core features, see the following:
Performance
When running NVTabular on the Criteo 1TB Click Logs Dataset using a single V100 32GB GPU, feature engineering and preprocessing was able to be completed in 13 minutes. Furthermore, when running NVTabular on a DGX-1 cluster with eight V100 GPUs, feature engineering and preprocessing was able to be completed within three minutes. Combined with HugeCTR, the dataset can be processed and a full model can be trained in only six minutes.
The performance of the Criteo DRLM workflow also demonstrates the effectiveness of the NVTabular library. The original ETL script provided in Numpy took over five days to complete. Combined with CPU training, the total iteration time is over one week. By optimizing the ETL code in Spark and running on a DGX-1 equivalent cluster, the time to complete feature engineering and preprocessing was reduced to three hours. Meanwhile, training was completed in one hour.
Installation
Prior to installing NVTabular, ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
CUDA version 10.1+
Python version 3.7+
NVIDIA Pascal GPU or later
NOTE: NVTabular will only run on Linux. Other operating systems are not currently supported.
Installing NVTabular Using Conda
NVTabular can be installed with Anaconda from the nvidia channel by running the following command:
conda install -c nvidia -c rapidsai -c numba -c conda-forge nvtabular python=3.7 cudatoolkit=11.0
If you’d like to create a full conda environment to run the example notebooks, do the following:
Use the environment files that have been provided to install the CUDA Toolkit (11.0 or 11.2).
Clone the NVTabular repo and run the following commands from the root directory:
conda env create -f=conda/environments/nvtabular_dev_cuda11.2.yml conda activate nvtabular_dev_11.2 python -m ipykernel install --user --name=nvt pip install -e . jupyter notebook
When opening a notebook, be sure to select
nvtfrom theKernel->Change Kernelmenu.
Installing NVTabular with Docker
NVTabular Docker containers are available in the NVIDIA Merlin container repository. There are four different containers:
| Container Name | Container Location | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| merlin-inference | https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/containers/nvidia:merlin:merlin-inference | NVTabular, HugeCTR, and Triton Inference |
| merlin-training | https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/containers/nvidia:merlin:merlin-training | NVTabular and HugeCTR |
| merlin-tensorflow-training | https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/containers/nvidia:merlin:merlin-tensorflow-training | NVTabular, TensorFlow, and HugeCTR Tensorflow Embedding plugin |
| merlin-pytorch-training | https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/containers/nvidia:merlin:merlin-pytorch-training | NVTabular and PyTorch |
To use these Docker containers, you’ll first need to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit to provide GPU support for Docker. You can use the NGC links referenced in the table above to obtain more information about how to launch and run these containers. To obtain more information about the software and model versions that NVTabular supports per container, see Support Matrix.
Notebook Examples and Tutorials
We provide a collection of examples, use cases, and tutorials as Jupyter notebooks that demonstrate how to use the following datasets:
MovieLens25M
Outbrain Click Prediction
Criteo 1TB Click Logs
RecSys2020 Competition Hosted by Twitter
Rossmann Sales Prediction
Each Jupyter notebook covers the following:
Feature engineering and preprocessing with NVTabular
Advanced workflows with NVTabular
Accelerated dataloaders for TensorFlow and PyTorch
Scaling to multi-GPU and multi-node systems
Integrating NVTabular with HugeCTR
Deploying to inference with Triton
Feedback and Support
If you’d like to contribute to the library directly, see the Contributing.md. We’re particularly interested in contributions or feature requests for our feature engineering and preprocessing operations. To further advance our Merlin Roadmap, we encourage you to share all the details regarding your recommender system pipeline in this survey.
If you’re interested in learning more about how NVTabular works, see our NVTabular documentation. We also have API documentation that outlines the specifics of the available calls within the library.