End-to-end pipeline with NVIDIA Merlin
Transformers4Rec has a first-class integration with NVIDIA Merlin components, to build end-to-end GPU accelerated pipelines for sequential and session-based recommendation.
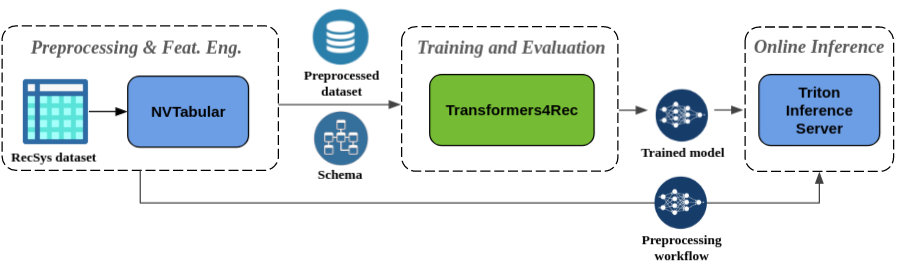
Integration with NVTabular
NVTabular is a feature engineering and preprocessing library for tabular data that is designed to easily manipulate terabyte scale datasets and train deep learning (DL) based recommender systems.
It has some popular techniques to deal with categorical and numerical features like Categorify, Normalize, Bucketize, TargetEncoding, DifferenceLag, to name a few supported, and also allow for the definition of custom transformations (LambdaOp) using cuDF data frame operations.
Usually the input RecSys datasets contain one example per user interaction. For sequential recommendation, the training example is a sequence of user interactions, and for session-based recommendation it is a sequence of session interactions. In practice, each interaction-level feature needs to be converted to a sequence grouped by user/session and their sequence length must match, as each position of the sequence corresponds to one interaction. You can see in Fig. 4 how the preprocessed parquet should look like.
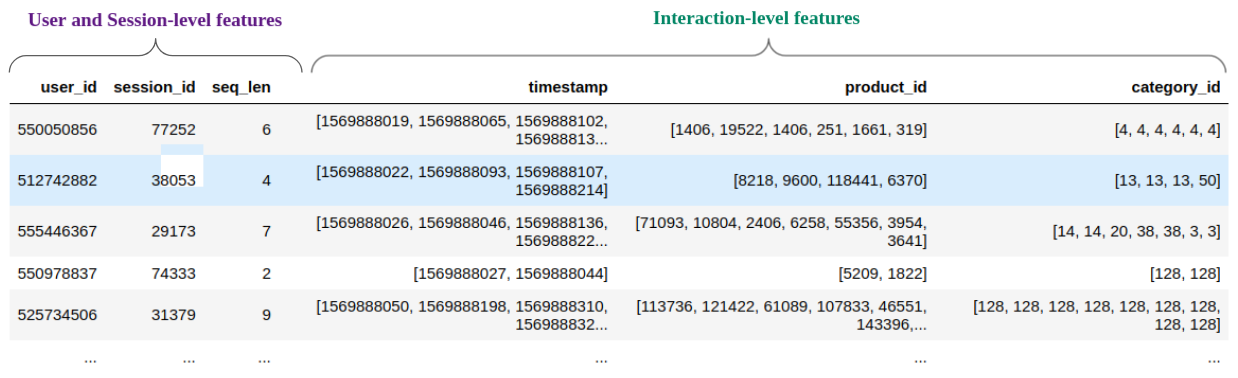
NVTabular can easily prepare such data with the Groupby op, which allows grouping by a categorical column (e.g. user id, session id), sorting by another column (e.g. timestamp) and aggregating other columns as sequences (list) or by taking the first or last element of the sequence, as exemplified below.
groupby_features = [
'user_id', 'session_id', 'product_id', 'category_id', 'timestamp'
] >> ops.Groupby(
groupby_cols=['session_id'],
sort_cols=['timestamp'],
aggs={
'product_id': 'list',
'category_id': 'list',
'timestamp': ['first', 'last'],
},
)
Outputs
NVTabular outputs parquet files with the preprocessed data. The parquet files can be (Hive) partitioned by a categorical column (e.g. day, company), as in the following example.
nvt_output_path ='./output'
partition_col = ['day']
nvt.Dataset(dataset).to_parquet(nvt_output_path, partition_on=[partition_col])
NVTabular also outputs a schema file in the protobuf text format (schema.pbtxt) together with the parquet files. The schema file contains statistics obtained during the preprocessing, like the cardinality of categorical features, the max sequence length for sequential features. NVTabular also allows the association of tags for features (e.g. to indicate what is the item id, what are item and user features, what are categorical or continuous features). You can see here an example of a such schema in Protobuf Text format.
If you don’t use NVTabular to preprocess your data, you can also instantiate a Schema via code manually (see examples).
The NVTabular workflow can be saved after workflow.fit() is called, so that the same preproc workflow can be applied to new input data, either in batch or online (via integration with Triton Inference Server), described in the next section.
# Instantiates an NVTabular dataset
dataset = nvt.Dataset([os.path.join(INPUT_PATH, "*.parquet")], part_size="100MB")
# Perform a single pass over the dataset to collect columns statistics
workflow.fit(dataset)
# Applies the transform ops to the dataset
new_dataset = workflow.transform(dataset)
# Saves the preprocessed dataset in parquet files
new_dataset.to_parquet("/path")
# Saves the "fitted" preprocessing workflow
workflow.save(os.path.join(OUTPUT_PATH, "workflow"))
Integration with Triton Inference Server
NVIDIA Triton Inference Server (TIS) simplifies the deployment of AI models at scale in production. TIS is a cloud and edge inferencing solution optimized to deploy machine learning models both for GPUs and CPUs and it supports a number of different deep learning frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch.
An end-to-end ML/DL pipeline consists of preprocessing and feature engineering (ETL), model training, and model deployment for inference. Model deployment in production is the critical step of this pipeline since it enables model inference for practical business decisions. In the production setting, we want to apply to the input data the same transformation ops done during training (ETL). That is, the preprocessing ops, like standardizing continuous features and encoding categorical features, should be compatible with the statistics of the original data, before feeding data to the deep learning model. NVTabular supports such a scenario, allowing the export of the preproc workflow together with a PyTorch or Tensorflow trained model in a single ensemble pipeline to be served on TIS.
The TIS integration enables the deployment of deep learning recommender models at scale with GPU acceleration. Transformers4Rec currently supports exporting a model trained with the PyTorch API to Triton Inference Server using the Python backend. In the upcoming release of Transformers4Rec, we will support deployment of models trained with Tensorflow to TIS.
To see how you can deploy a large and complex recommender workflow to production with only a few lines of code, visit our end-to-end-session-based recommendation and tutorial example notebooks for inference with Triton examples.