Why Transformers4Rec?
The relationship between NLP and RecSys
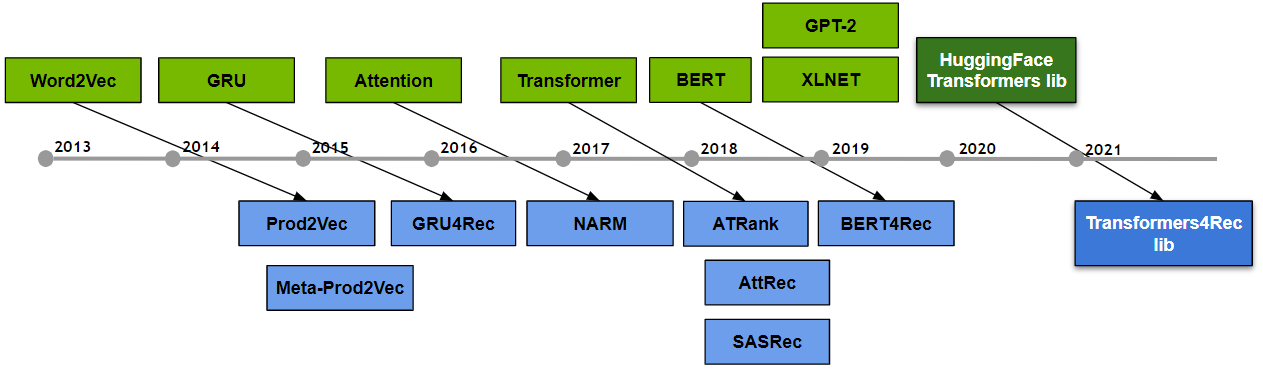
Over the past decade there has been a trend toward leveraging and adapting approaches proposed by Natural Language Processing (NLP) research like Word2Vec, GRU, and Attention for recommender systems (RecSys). The phenomena is especially noticeable for sequential and session-based recommendation where the sequential processing of users interactions is analogous to the language modeling (LM) task and many key RecSys architectures have been adapted from NLP, like GRU4Rec – the seminal Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)-based architecture for session-based recommendation.
More recently, Transformer architectures have become the dominant technique over convolutional and recurrent neural networks for language modeling tasks. Because of their efficient parallel training, these architectures scale well with training data and model size, and are effective at modeling long-range sequences.
Transformers have similarly been applied to sequential recommendation in architectures like SASRec, BERT4Rec and BST, providing higher accuracy than architectures based on CNN and RNNs, as can be seen in their reported experiments and also in our [ACM RecSys’21 paper](Updated references do paper URL in docs).
You can read more about this relationship between NLP and RecSys and the evolution of the architectures for sequential and session-based recommendation towards Transformers in our paper too.
Integration with HuggingFace Transformers
Transformers4Rec integrates with the HuggingFace (HF) Transformers library, allowing RecSys researchers and practitioners to easily experiment with the latest and state-of-the-art NLP Transformer architectures for sequential and session-based recommendation tasks and deploy those models into production.
The HF Transformers was “established with the goal of opening up advancements in NLP to the wider machine learning community”. It has become very popular among NLP researchers and practitioners (more than 900 contributors), providing standardized implementations of the state-of-the-art Transformer architectures (more than 68 and counting) produced by the research community, often within days or weeks of their publication.
HF Transformers is designed for both research and production. Models are composed of three building blocks: (a) a tokenizer, which converts raw text to sparse index encodings; (b) a transformer architecture; and © a head for NLP tasks, like Text Classification, Generation, Sentiment Analysis, Translation, Summarization, among others.
In Transformers4Rec we leverage from HF Transformers only the transformer architectures building block (b) and their configuration classes. Transformers4Rec provides additional blocks necessary for recommendation, e.g., input features normalization and aggregation, and heads for recommendation and sequence classification/prediction. We also extend their Trainer class to allow for the evaluation with RecSys metrics.